How does Indian government generate its revenue?
The 5 major sources of revenue for the Government are Goods and Services Tax (GST), Income tax, corporation tax, non-tax revenues, and union excise duties. On the other hand, non-tax revenue is the recurring income earned by the government from sources other than taxes.
The revenue budget consists of revenue receipts of the Government of India and the expenditure met using that revenue. The revenue budget details the sources from which the revenue is coming to the government. The government’s sources of revenue are taxes collected from people and corporations. The government also makes investments through various instruments and receives interest and dividends on those. Its non-tax revenue includes the disinvestments that the government does in the companies where it holds stakes. This also accounts for the revenue of the government.

Source of Tax Revenue
The government generates its revenue from taxes and several other non-tax revenue sources. Tax is one of the major sources of revenue for the government to carry out its work. Tax revenue can be classified into a few major categories corporation tax, tax on income, Customs, Union excise duties, service tax, and several others.
Corporation tax is the biggest source of revenue for the government. Public and private companies registered under the Companies Act, 1956, are liable to pay corporation tax. Corporation tax is levied on the net income of the company. The collection, surcharge, cess, and other receipts make up a huge chunk of the revenue.
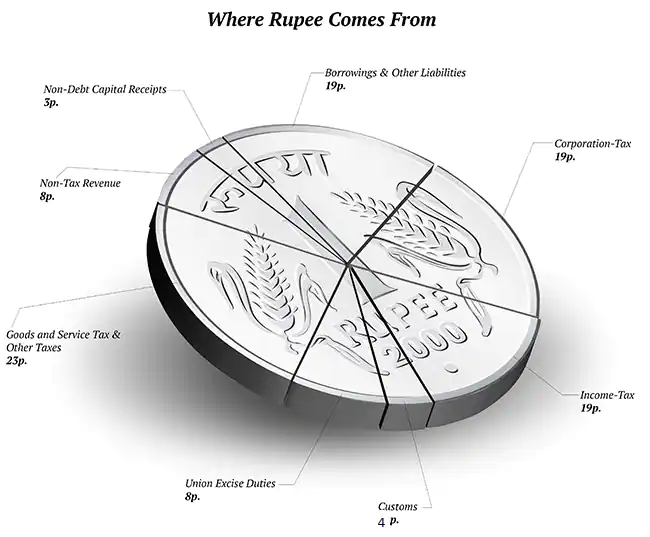
The above pick is explaining that how the Indian Government earns revenue from sources after the coming of the BJP party in 2014 Central Government this is shown that in upcoming times the government companies are moved into privatization due to control of Indian Government companies are not more performed due to some problems like Earning, Profit, liquidity &, etc all like this factors are creating to get into take in competition with other private companies.
Direct Tax
In this, the taxes are directly levied on a person. The major source of tax revenue in India is generated through direct taxes. Some of the common direct taxes in India are income tax, securities transaction tax, corporate income tax, banking cash transaction tax, etc. We will explain to you, in brief, some of these direct taxes in India.
Income Tax
The person whose income falls into a particular taxable category has to pay a certain amount of tax. This tax is called income tax. Also, the income tax department in India falls under CBDT. It is also a part of the department of revenue that comes under the ministry of finance. Also, income tax is one of the key sources of funds that the government uses to fund other activities.
Customs Duty
This is a typical indirect tax that is levied on goods imported to India. Also, it is levied on goods that are exported from India. The basic law that governs the collection of these taxes is the customs act, of 1962.
Corporate Taxes
Indian taxes are divided into two types: One is Direct Taxes and the other is Indirect Taxes. Talking direct taxes, it is levied on the income that different types of business entities earn in a financial year. There are different types of taxpayers registered with the Income tax department and they pay taxes at different rates. For eg, An individual and a company being a taxpayer are not taxed at the same rate.
- Personal Income Tax: The income tax paid by the individual taxpayers is the personal income tax. Individuals get taxed on the basis of tax slabs at different rates.
- Corporate Tax: The income-tax paid by domestic companies, and foreign companies on their income in India is corporate income tax (CIT). The CIT is at a specific rate as prescribed by the income tax act subject to the changes in the rates in the union budget every year.
For the purpose of calculation of taxes under the Income tax act, the types of companies can be defined as under:
- Domestic Company: Domestic company is one that is registered under the Companies Act of India and also includes the company registered in foreign countries having control and management wholly situated in India. A domestic company includes private as well as public companies.
- Foreign Company: Foreign company is one that is not registered under the companies act of India and has control & management located outside India.
The steps include the launch of ‘Operation Clean Money’ after the demonetization of old higher denomination currency for collection, collation, and analysis of information on cash transactions, extensive use of information technology, and data analytics tools for identification of high-risk cases, expeditious e-verification of suspect cases and enforcement actions.
The blueprint will suggest ways to attain less carbon-intensive and more technology-driven growth, while also narrowing income inequality.