Thyroid Gland & Thyroid Hormones
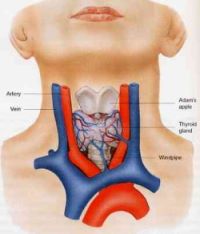
The thyroid gland lies in the front of the neck between the skin and the voice box. It has a right and left lobe each about five centimetres in length and joined in the midline. The entire gland weighs less than an ounce (about 20 grams). Despite its small size it is an extremely important organ which controls our metabolism and is responsible for the normal working of every cell in the body. It achieves this by manufacturing the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) and secreting them into the bloodstream. Iodine is an important constituent of these hormones. There are four atoms of iodine in each molecule of thyroxine, hence the abbreviation T4, and three atoms of iodine in each molecule of triiodothyronine or T3.
 These 2 types of thyroid hormones are easily measurable in the blood, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). For technical reasons, it is easier and less expensive to measure the T4 level, so T3 is usually not measured on screening tests.
These 2 types of thyroid hormones are easily measurable in the blood, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). For technical reasons, it is easier and less expensive to measure the T4 level, so T3 is usually not measured on screening tests.
Please be clear on which test you are looking at. There continues to be some confusion among doctors, nurses, lab techs, and patients on which test is which. In particular, the "Total T3", "Free T3" and "T3 Uptake tests" are very confusing, and are not the same test.
Thyroxine (T4) : This shows the total amount of the T4. High levels may be due to hyperthyroidism, however technical artifact occurs when estrogen levels are higher from pregnancy, birth control pills or estrogen replacement therapy. A Free T4 (see below) can avoid this interference.
T3 Resin Uptake or Thyroid Uptake : This is a test that confuses doctors, nurses, and patients. First, this is not a thyroid test, but a test on the proteins that carry thyroid around in your bloodstream. Not only that, a high test number may indicate a low level of the protein! The method of reporting varies from lab to lab. The proper use of the test is to compute the free thyroxine index.
Free Thyroxine Index (FTI or T7) : A mathematical computation allows the lab to estimate the free thyroxine index from the T4 and T3 Uptake tests. The results tell us how much thyroid hormone is free in the bloodstream to work on the body. Unlike the T4 alone, it is not affected by estrogen levels.
Free T4 : This test directly measures the free T4 in the blood rather than estimating it like the FTI. It is a more reliable , but a little more expensive test. Some labs now do the Free T4 routinely rather than the Total T4.
Total T3 : This is usually not ordered as a screening test, but rather when thyroid disease is being evaluated. T3 is the more potent and shorter lived version of thyroid hormone. Some people with high thyroid levels secrete more T3 than T4. In these (overactive) hyperthyroid cases the T4 can be normal, the T3 high, and the TSH low. The Total T3 reports the total amount of T3 in the bloodstream, including T3 bound to carrier proteins plus freely circulating T3.
Free T3 : This test measures only the portion of thyroid hormone T3 that is "free", that is, not bound to carrier proteins.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) : This protein hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland and regulates the thyroid gland. A high level suggests your thyroid is underactive, and a low level suggests your thyroid is overactive.
Disclaimer : Our goal is to provide you with information that may be useful in attaining optimal health. Nothing in it is meant as a prescription or as medical advice. For more details, please contact your nearest doctor.
I’ll come back again to find out your upcoming post! Good job done!