Basic Knowledge about the Earth
The earth is in the third position from the sun and is the fifth largest planet in the solar system.
Shape of the Earth
 The earth is an oblate spheroid (ball flattened at the poles), i.e., almost spherical, flattened a little at the poles, and with a slight bulge at the centre (equator). The spinning (rotation) of the earth at a high speed has caused its mass to bulge at the equator and sinking at the poles.
The earth is an oblate spheroid (ball flattened at the poles), i.e., almost spherical, flattened a little at the poles, and with a slight bulge at the centre (equator). The spinning (rotation) of the earth at a high speed has caused its mass to bulge at the equator and sinking at the poles.
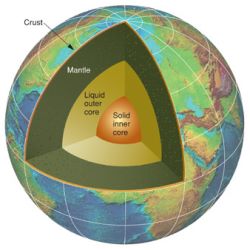
Structure of the Earth
The earth is made up of a number of concentric layers of material as in the bulb of an onion.
Composition of the Earth
The earth is made up of more than 100 different elements. The important ones are:
| Oxygen | 46.6% |
| Silicon | 27.72% |
| Aluminum | 8.13% |
| Iron | 5.01% |
| Calcium | 3.63% |
| Sodium | 2.85% |
| Potassium | 2.62% |
| Magnesium | 2.09% |
The earth has four distinct spheres:
- Lithosphere: Top crust which includes land surface and ocean floor. top crust which includes land surface and ocean floor. >
- Hydrosphere: Water surface which includes oceans, seas, rivers and lakes water surface which includes oceans, seas, rivers and lakes >
- Atmosphere: The cover of air that envelops the earth?s surface the cover of air that envelops the earth?s surface >
- Biosphere: The region where life exists the region where life exists >
Important Data about the Earth
| Diameter | At the equator At the poles Mean diameter |
12,756.32 km 12,713.54 km 12,734 km |
| Equatorial Radius | 6377 km | |
| Total Surface Area | 509,700,000 sq. km | |
| Total Land Area (29.08%) | 148,400,000 sq. km | |
| Total Water area (70.92%) | 361,300,000 sq. km | |
| Mean Distance from the Sun | 1,49,407,000 sq. km | |
| Time for rotation on its own Axis | 23 h, 56 min and 4.09 sec | |
| Period for Revolution around the Sun | 365 days, 6 hrs, 9 min and 9.54 sec | |
Earth’s Movements
The earth has two types of movements:
Rotation: The earth spins on its own imaginary axis from west to east once in 24 hours. It is also called diurnal or daily motion, which causes the formation of day and night.
| Longest days and nights | Northern Hemisphere |
Southern Hemisphere |
| Longest day (shortest night) | June 21 | December 22 |
| Shortest day (longest night) | December 21 | June 21 |
Days and nights are equal at the equator throughout the year because the circle of illumination always divides the equator into two equal parts.
Revolution: While rotating on its axis, the earth revolves around the sun, along an almost circular path (elliptical) called its orbit. It is also called annual motion or yearly motion because it takes one solar year to complete the journey i.e., 365 days or 365 days, 6 hours 9 minutes and 9.54 seconds. The earth?s revolution causes a change in season.
How Seasons Change?
 The earth’s axis is inclined at an angle of 66.50 to the plane of its orbit. As a result of this, the earth is in different positions while revolving around the sun. During the first half of the year the northern hemisphere tilts towards the sun resulting in the season of summer in the region. During the second half of the year the southern hemisphere tilts towards the sun and thus experiences summer and the northern hemisphere experiences winter during this period. The revolution causes the four seasons:
The earth’s axis is inclined at an angle of 66.50 to the plane of its orbit. As a result of this, the earth is in different positions while revolving around the sun. During the first half of the year the northern hemisphere tilts towards the sun resulting in the season of summer in the region. During the second half of the year the southern hemisphere tilts towards the sun and thus experiences summer and the northern hemisphere experiences winter during this period. The revolution causes the four seasons:
- Spring: When the sun is directly overhead the equator when the sun is directly overhead the equator >
- Summer: when the sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Cancer ? the north temperate zone experiences summer when the sun is directly overhead the tropic of cancer ? the north temperate zone experiences summer >
- Autumn: When the sun returns to the equator and the north temperate zone experiences the season of autumn when the sun returns to the equator and the north temperate zone experiences the season of autumn >
- Winter: The sun is at the Tropic of Capricorn and the north temperate zone experiences winter the sun is at the tropic of capricorn and the north temperate zone experiences winter >
Equinoxes: Equinoxes are dates when the nights and days are equal. During these days the sun shines directly over the equator. March 21 is called vernal equinox and September 23 is called autumnal equinox.
Solstice: The time of the year when the difference between the length of days and nights is the largest it is referred to as solstice.
On, or around June 21, the North Pole tilts towards the sun and the sun shine directly over the Tropic of Cancer, which is called summer solstice. On or around December 22, the earth is at the opposite end of its orbit, as a result, the South Pole tilts towards the sun and the North Pole away from it. This is called winter solstice.
Eclipses: When the light of the sun or the moon is obscured by another body the sun or moon is said to be in eclipse.
Lunar Eclipse: When the earth comes between the moon and the sun, the shadow cast by the earth on the moon results in a lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipse occurs only on a full moon day but not on every full moon day.
Solar eclipse: A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day when the moon is in line with the sun. However, solar eclipse does not occur on every new moon day.